NA
Definition of NA
Returns the "value not available" error, `#N/A`.
Sample Usage
NA()
Syntax
NA()
Notes
#N/Ais an error, so both theISNAandISERRORfunctions will returnTRUE. UseISERRto find errors which are not#N/A.Typing
=NA()into a cell is equivalent to directly entering the error value#N/A.#N/Ais used to mark missing information and to indicate to functions operating on ranges or cells containing such values to halt calculation. For instance, if cellB2contained the result of anIFstatement:=IF(ISBLANK(A1),0,A1)andB2was subsequently involved in a sum or other formula, that formula would assume thatB2held the correct information. By altering the formula inB2to=IF(ISBLANK(A1),NA(),A1), any subsequent operation onB2would halt upon encountering the#N/Aerror, and return that error.#N/Aerrors indicate missing information and signal functions using to cease calculation. Use the#N/Avalue instead of0orresults. For example, if
A1contains the value#N/Aor=NA(), the formula=A1+A2will evaluate to#N/A.
See Also
ISNA: Checks whether a value is the error `#N/A`.
ISERROR: Checks whether a value is an error.
ISERR: Checks whether a value is an error other than `#N/A`.
In order to use the NA formula, start with your edited Excellentable
Then type in the NA Formula in the area you would like to display the outcome:
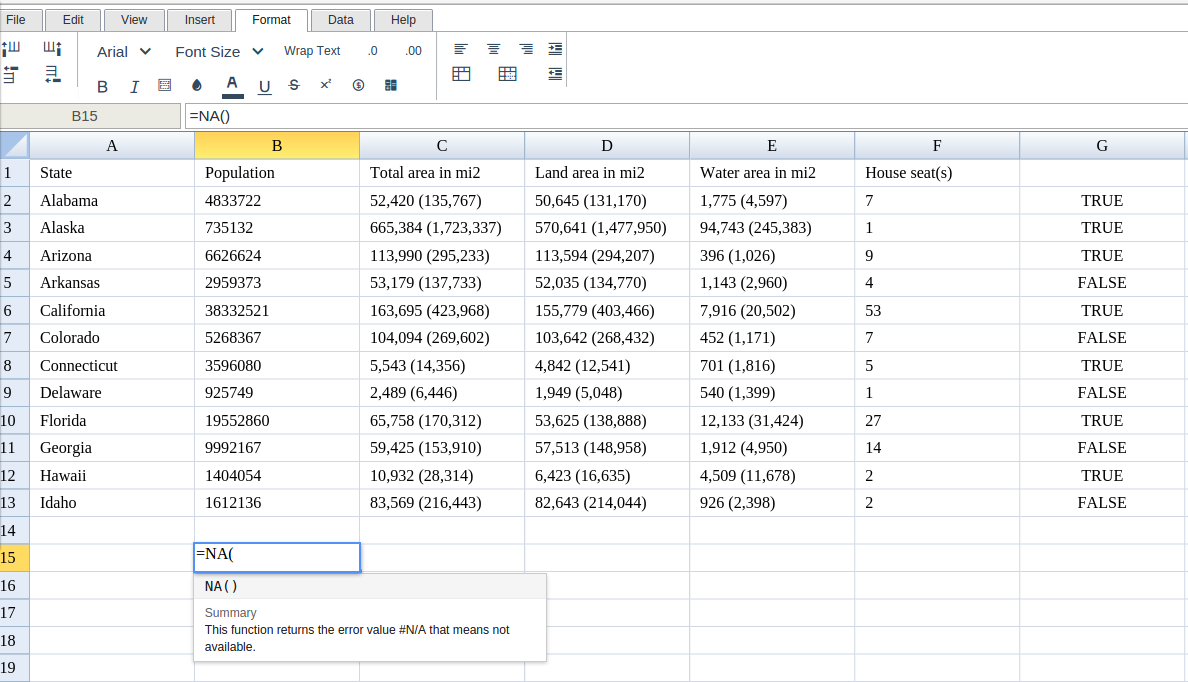
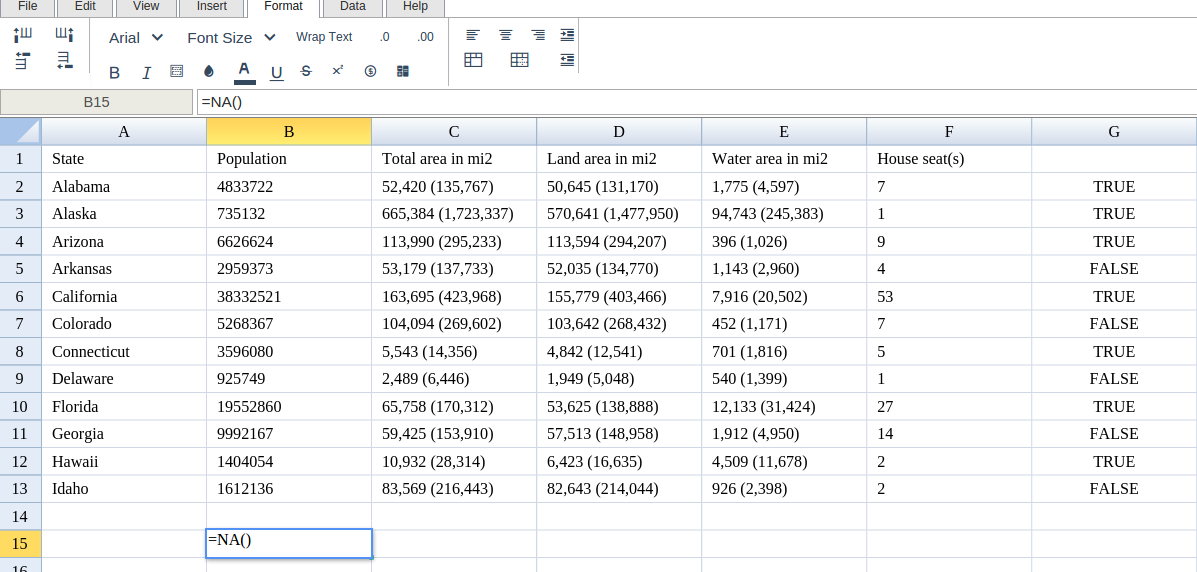
Type in the complete NA formula for a cell as shown below:
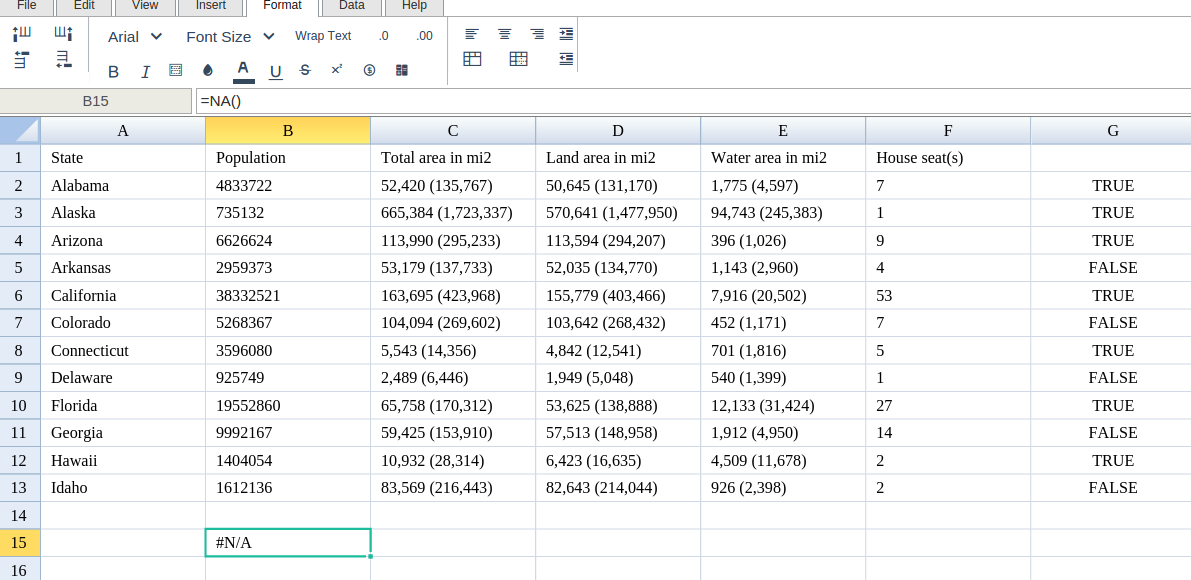
Excellentable will generate the outcome when hitting enter.
A
|
B
|
C
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
1
|
|||
2
|
|||
3
|
|||
4
|
|||
5
|
|||
6
|
|||
7
|
|||
8
|
|||
9
|
|||
10
|
|||
11
|
|||
12
|
|||
13
|
|||
14
|
|||
15
|
D
|
E
|
F
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
1
|
G
|
|
|---|---|
1
|
