PI
Definition
Returns the value of Pi to 14 decimal places.
Sample Usage
PI()
Syntax
PI()
See Also
TANH: Returns the hyperbolic tangent of any real number.
TAN: Returns the tangent of an angle provided in radians.
SINH: Returns the hyperbolic sine of any real number.
SIN: Returns the sine of an angle provided in radians.
RADIANS: Converts an angle value in degrees to radians.
DEGREES: Converts an angle value in radians to degrees.
COSH: Returns the hyperbolic cosine of any real number.
COS: Returns the cosine of an angle provided in radians.
ATANH: Returns the inverse hyperbolic tangent of a number.
ATAN2: Returns the angle between the x-axis and a line segment from the origin (0,0) to specified coordinate pair (`x`,`y`), in radians.
ATAN: Returns the inverse tangent of a value, in radians.
ASINH: Returns the inverse hyperbolic sine of a number.
ASIN: Returns the inverse sine of a value, in radians.
ACOSH: Returns the inverse hyperbolic cosine of a number.
ACOS: Returns the inverse cosine of a value, in radians.
In order to use the PI formula, start with your edited Excellentable.
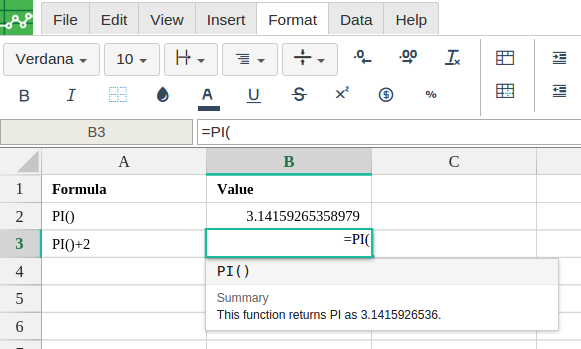
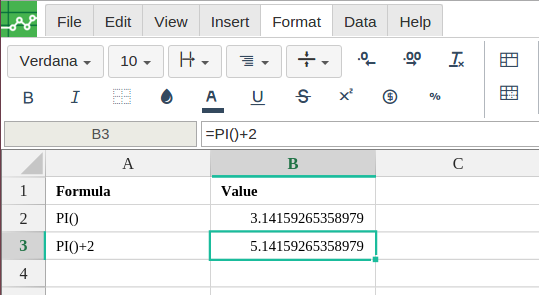
Excellentable generates the outcome:
A
|
B
|
|
|---|---|---|
1
|
||
2
|
||
3
|
