POISSON
Definition of POISSON
Returns the value of the Poisson distribution function (or Poisson cumulative distribution function) for a specified value and mean.
Sample Usage
POISSON(2.4,1,FALSE)
POISSON(A2,A3,TRUE)
Syntax
POISSON(x, mean, cumulative)
x- The input to the Poisson distribution function.mean- The mean (mu) of the Poisson distribution function.cumulative- Whether to use the Poisson cumulative distribution function rather than the distribution function..
Notes
The Poisson distribution function is typically used to calculate the number of 'arrivals' or 'events' over a period of time, such as the number of network packets or login attempts given some mean.
If
cumulativeisTRUEthenPOISSONreturns the probability ofxor fewer events, otherwise the probability of exactlyxevents.
See Also
WEIBULL: Returns the value of the Weibull distribution function (or Weibull cumulative distribution function) for a specified shape and scale.
NORMSINV: Returns the value of the inverse standard normal distribution function for a specified value.
NORMSDIST: Returns the value of the standard normal cumulative distribution function for a specified value.
NORMINV: Returns the value of the inverse normal distribution function for a specified value, mean, and standard deviation.
NORMDIST: Returns the value of the normal distribution function (or normal cumulative distribution function) for a specified value, mean, and standard deviation.
NEGBINOMDIST: Calculates the probability of drawing a certain number of failures before a certain number of successes given a probability of success in independent trials.
LOGNORMDIST: Returns the value of the log-normal cumulative distribution with given mean and standard deviation at a specified value.
LOGINV: Returns the value of the inverse log-normal cumulative distribution with given mean and standard deviation at a specified value.
EXPONDIST: Returns the value of the exponential distribution function with a specified lambda at a specified value.
BINOMDIST: Calculates the probability of drawing a certain number of successes (or a maximum number of successes) in a certain number of tries given a population of a certain size containing a certain number of successes, with replacement of draws.
In order to use the POISSON formula, start with your edited Excellentable
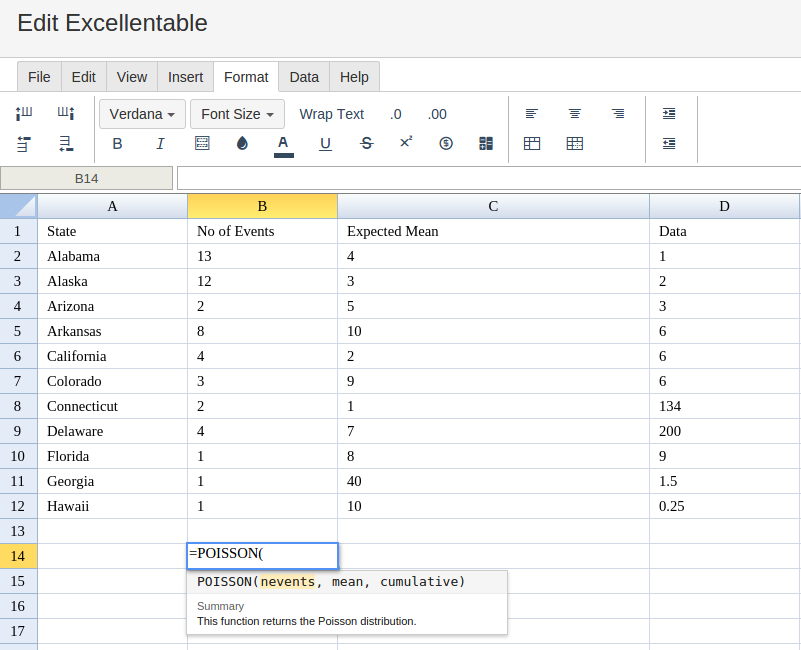
Then type in the POISSON Formula in area you would like to display the outcome:
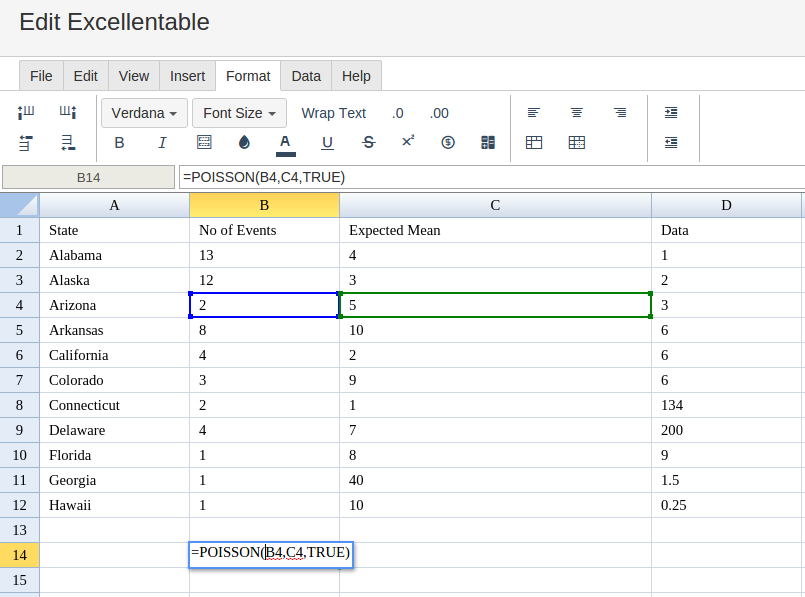
Type in the complete POISSON formula for a cell as shown below:
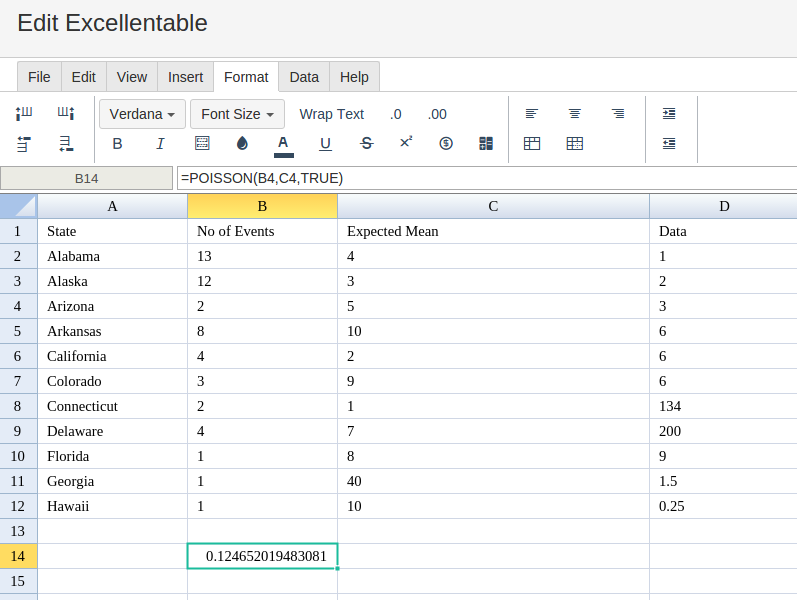
Excellentable will generate the outcome when hitting enter.
A
|
B
|
C
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
1
|
|||
2
|
|||
3
|
|||
4
|
|||
5
|
|||
6
|
|||
7
|
|||
8
|
|||
9
|
|||
10
|
|||
11
|
|||
12
|
|||
13
|
|||
14
|
D
|
|
|---|---|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
11
|
|
12
|
|
13
|
|
14
|
arrivals, x