SEARCH
Definition of SEARCH:
Returns the position at which a string is first found within text, ignoring case.
Sample Usage
SEARCH("n",A2)
SEARCH("wood","How much wood can a woodchuck chuck",14)
Syntax
SEARCH(search_for, text_to_search, [starting_at])
search_for- The string to look for withintext_to_search.text_to_search- The text to search for the first occurrence ofsearch_for.starting_at- [ OPTIONAL -1by default ] - The character withintext_to_searchat which to start the search.
Notes
SEARCHis not case-sensitive, meaning that uppercase and lowercase letters do not matter. For example, "abc" will match "ABC". To compare text where case matters, use theFINDfunction.- Ensure that
search_forandtext_to_searchare not supplied in reverse order, or the#VALUE!error will likely be returned. The arguments are supplied in a different order than other text functions such asSPLITandSUBSTITUTE. - It's recommended to use a function such as
IFERRORto check for cases when there aren't matches to the search.
See Also
SUBSTITUTE: Replaces existing text with new text in a string.
SPLIT: Divides text around a specified character or string, and puts each fragment into a separate cell in the row.
FIND: Returns the position at which a string is first found within text, case-sensitive.
IFERROR: Returns the first argument if it is not an error value, otherwise returns the second argument if present, or a blank if the second argument is absent.
Step 1. To use the SEARCH Formula, start with the Excellentable you would like to edit.
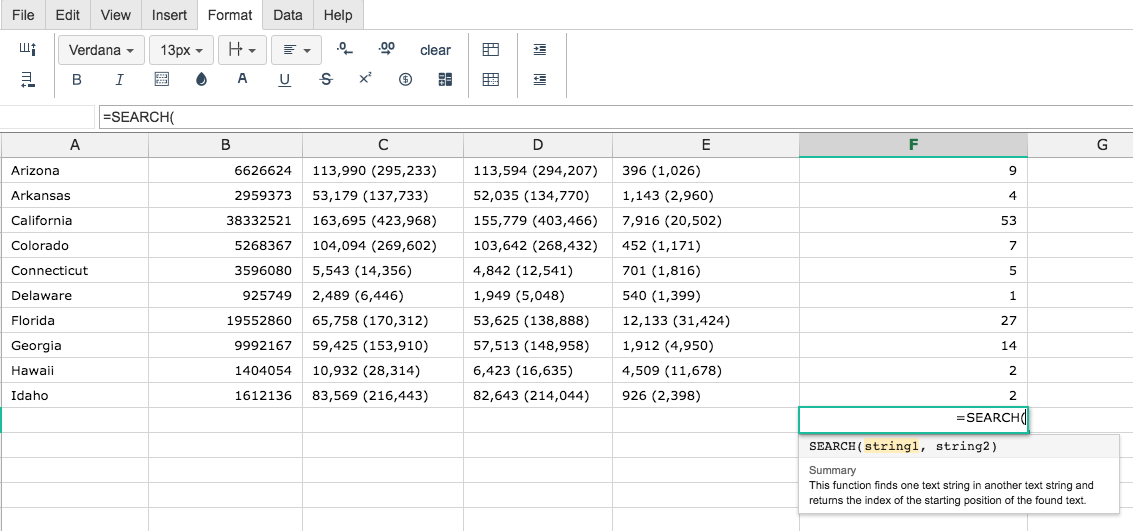
Step 2. Then type the SEARCH formula into the cell you have chosen to display the outcome:
Step 3. Fill in the 2 values.
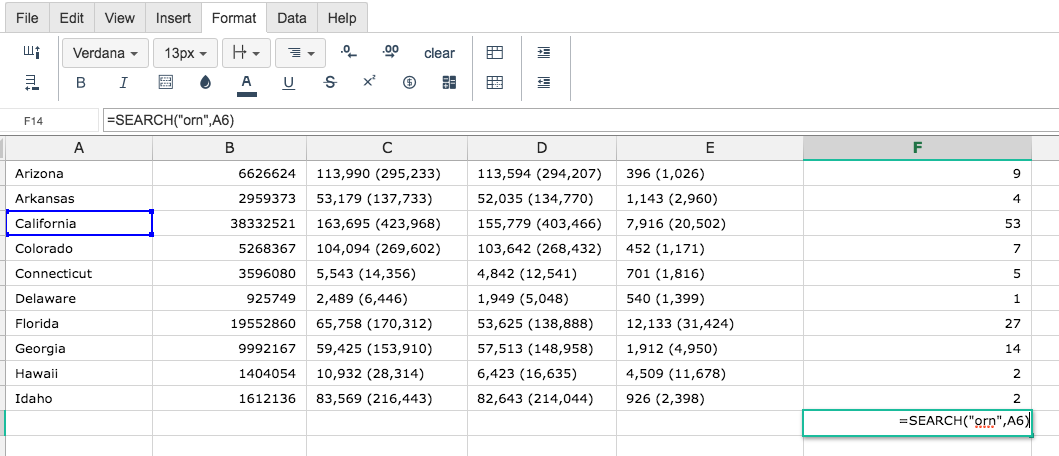
By adding the values you would like to calculate, Excellentable generates the outcome:
A
|
B
|
C
|
D
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
1
|
||||
2
|
||||
3
|
||||
4
|
||||
5
|
||||
6
|
||||
7
|
||||
8
|
||||
9
|
||||
10
|
||||
11
|
||||
12
|
||||
13
|
||||
14
|
E
|
F
|
|
|---|---|---|
1
|
