T.TEST
Definition
Returns the probability associated with a Student's t-Test. Use T.TEST to determine whether two samples are likely to have come from the same two underlying populations that have the same mean.
Sample Usage
Syntax
T.TEST(array1,array2,tails,type)
The T.TEST function syntax has the following arguments:
Array1 Required. The first data set.
Array2 Required. The second data set.
Tails Required. Specifies the number of distribution tails. If tails = 1, T.TEST uses the one-tailed distribution. If tails = 2, T.TEST uses the two-tailed distribution.
Type Required. The kind of t-Test to perform.
Parameters
If type equals | This test is performed |
1 | Paired |
2 | Two-sample equal variance (homoscedastic) |
3 | Two-sample unequal variance (heteroscedastic) |
Remarks
If array1 and array2 have a different number of data points, and type = 1 (paired), T.TEST returns the #N/A error value.
The tails and type arguments are truncated to integers.
If tails or type is nonnumeric, T.TEST returns the #VALUE! error value.
If tails is any value other than 1 or 2, T.TEST returns the #NUM! error value.
T.TEST uses the data in array1 and array2 to compute a non-negative t-statistic. If tails=1, T.TEST returns the probability of a higher value of the t-statistic under the assumption that array1 and array2 are samples from populations with the same mean. The value returned by T.TEST when tails=2 is double that returned when tails=1 and corresponds to the probability of a higher absolute value of the t-statistic under the “same population means” assumption.
In order to use the T.TEST formula, start with your edited Excellentable:
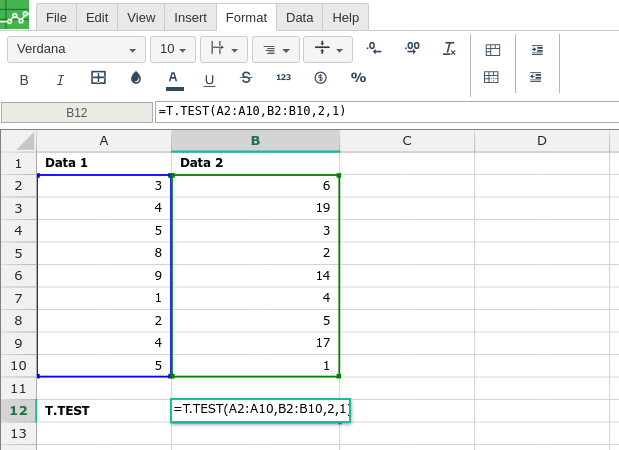
Then type in the T.TEST formula in the area you would like to display the outcome:
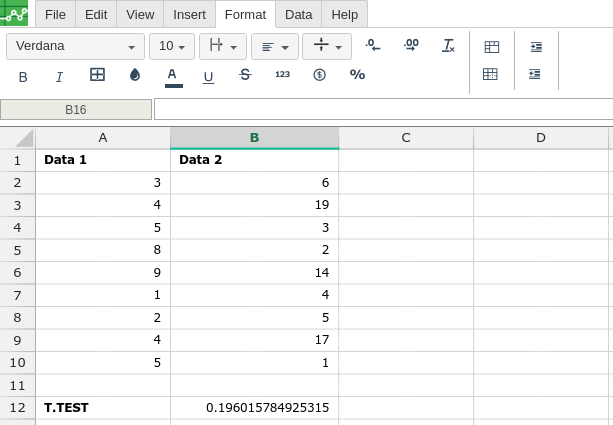
By adding the values you would like to calculate the T.TEST formula for, Excellentable will generate the outcome:
A
|
B
|
|
|---|---|---|
1
|
||
2
|
||
3
|
||
4
|
||
5
|
||
6
|
||
7
|
||
8
|
||
9
|
||
10
|
||
11
|
||
12
|
